Contractors scan floors inside Jana Elementary School in Missouri during testing done in October 2022. (Photo: USACE/JP Rebello)
New legislation that would require the cleanup of Jana Elementary School in suburban St. Louis was introduced in the Senate by Sen. Josh Hawley (R., Mo.). The Justice for Jana Elementary Act would also order the United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) to test all properties in the Hazelwood School District, of which Jana Elementary is a part.
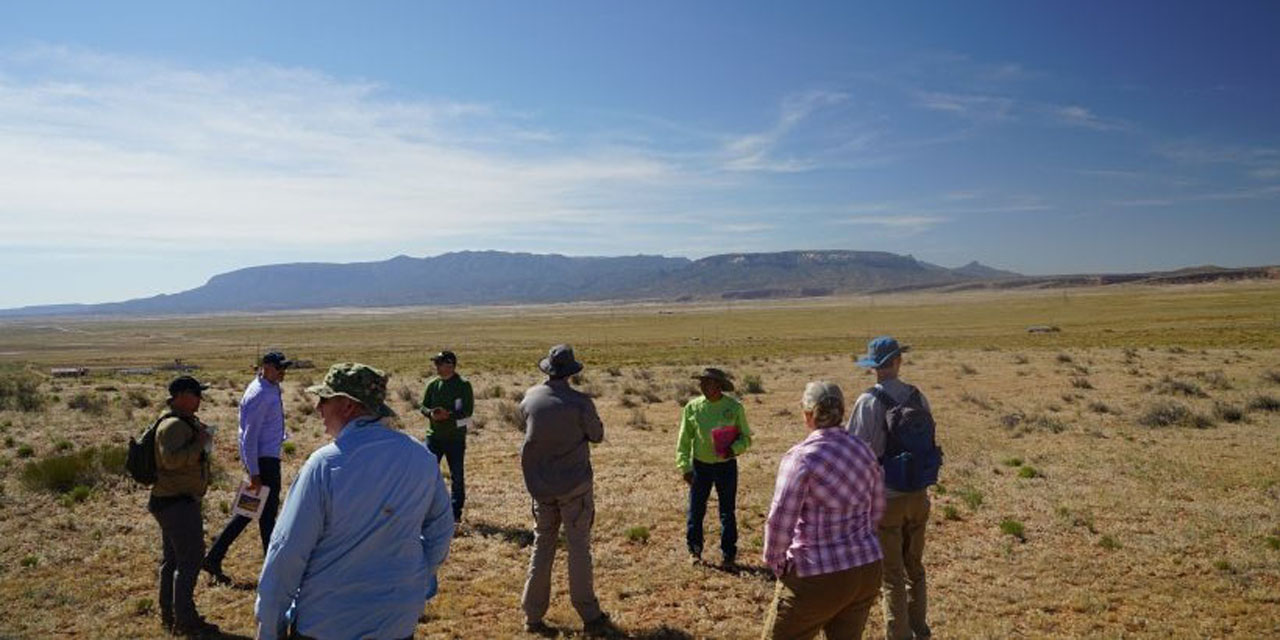
DRUM program members and others visit mine sites in the Navajo Nation during the spring of 2022. (Photo: DOE-LM)
The Department of Energy’ Office of Legacy Management (LM) will be conducting verification and validation work at abandoned uranium mines in the Navajo Nation of northeastern Arizona during the fall field season, which runs from mid-October to mid-December.
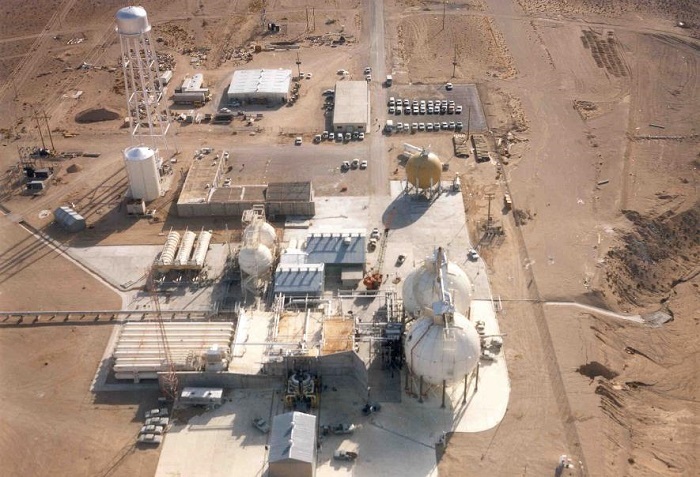
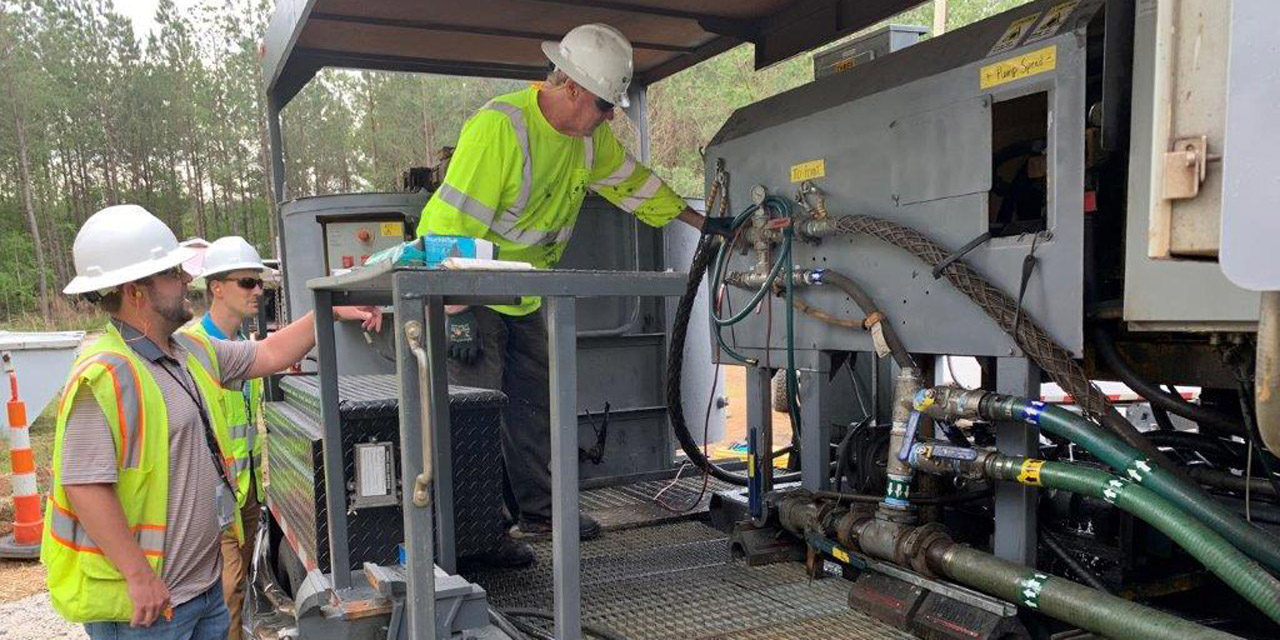
SRNS environmental engineers Bryce Garner (left) and Adam Willey (center) ask questions of lead operator Daniel Ferrell (right), from field services contractor Cascade Environmental, as he describes how equipment injects oil and iron into the Savannah River Site’s groundwater. (Photo: DOE)
In this week’s “EM Update,” the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) reports that its contractor Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS) has successfully reduced degreasing solvents in the aquifer beneath the Savannah River Site in South Carolina using a technology that injects a form of iron and oil into groundwater.
“The oil attracts the Cold War[–era] cleaning solvents while the iron degrades and neutralizes the contamination,” said Shannan Lucero, SRNS manager for area closure projects.
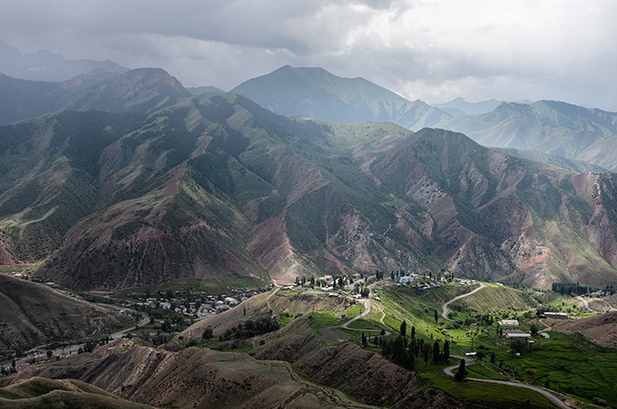
A view of the village of Min Kush in central Kyrgyzstan. (Photo: EBRD)
The remediation of two former Soviet-era uranium mining sites in Kyrgyzstan has been completed on schedule and below budget, despite difficulties caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) announced on March 28.
A rendering of Canadian Nuclear Laboratories’ proposed Near Surface Disposal Facility. (Image: CNL)
Canadian Nuclear Laboratories (CNL) is asking its stakeholders (members of the public, industry, elected officials, and employees) to support a proposal to construct the Near Surface Disposal Facility (NSDF) to dispose of legacy radioactive waste at the Chalk River Laboratories in Ontario.
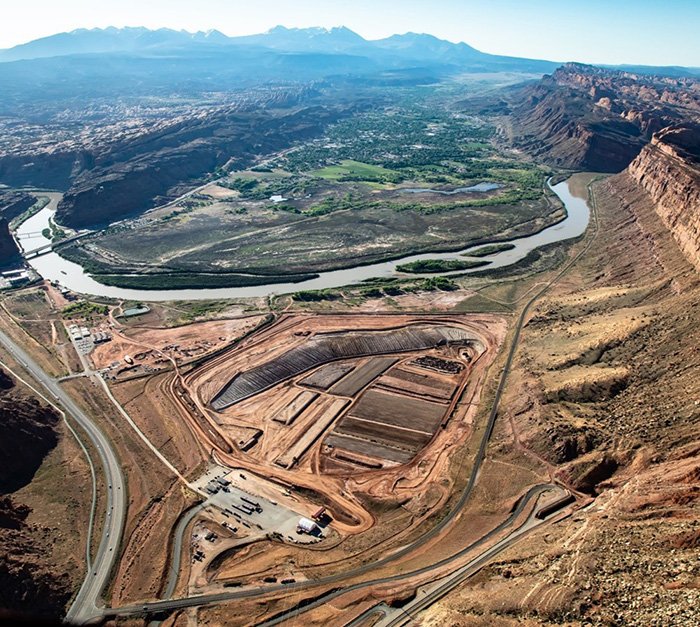
The Moab cleanup site in Utah in 2018. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (DOE-EM) has awarded a cleanup contract to North Wind Portage, Inc. for completion of environmental remediation of a uranium ore processing site near Moab, Utah. North Wind Portage is located in Idaho Falls, Idaho.
More information about the Moab project is available here.
An SRNS subcontractor technician takes radiological readings of soil near Lower Three Runs, part of a major project to complete the cleanup of a contaminated 25-mile-long stream corridor at SRS. (Photo: DOE) (CLICK TO SEE FULL PHOTO)
Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS), the Department of Energy’s management and operating contractor for the Savannah River Site in South Carolina, has reached an agreement with the state of South Carolina and federal environmental regulators on the final cleanup of a 25-mile-long stream corridor at the site that was radiologically contaminated as a result of operations during the Cold War.
The corridor consists of Par Pond, nine miles of canals adjacent to the pond, and a stream named Lower Three Runs. The stream begins near the center of the site, just above Par Pond, and winds its way southward across SRS.
The 100-BC Area (in green) within the Hanford Site. (Image: DOE)
Soil and groundwater contamination at the Hanford Site’s 100-BC Area will be treated under a record of decision (ROD) signed by the Department of Energy and the Environmental Protection Agency, with the concurrence of the Washington State Department of Ecology.
The EU’s Massimo Garribba (left) and the IAEA’s Lydie Evrard met at last week’s 65th IAEA General Conference to extend a 2013 cooperation agreement. (Photo: C./Silva Villareal)
Some of the major achievements of the nuclear safety cooperation agreement between the International Atomic Energy Agency and the European Union (EU) include more than 100 nuclear safety review missions, environmental remediation at former uranium sites in Central Asia, and more effective radioactive waste management in Africa.
U.S. Forest Service employees Secunda Hughes (left) and Andrew Thompson inspect irrigation piping and sprinkler heads, part of a 62-acre pine plantation used to safely disperse tritium at the Savannah River Site.
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) is managing the release of tritiated water using a 62-acre plantation of pine trees and other natural resources to limit radioactively contaminated groundwater from reaching waterways on the Savannah River Site in South Carolina.
An archive photo of the Nevada National Security Site’s Test Cell C complex, which is being prepared for demolition and closure. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy is preparing to demolish two large, complex facilities at the Nevada Nuclear Security Site with ties to historical nuclear propulsion rocket development and testing programs. The DOE’s Environmental Management (EM) Nevada Program and its environmental program services contractor, Navarro Research and Engineering, have begun characterization and hazard reduction work on the site’s Engine Maintenance, Assembly, and Disassembly (EMAD) and Test Cell C (TCC) complexes.
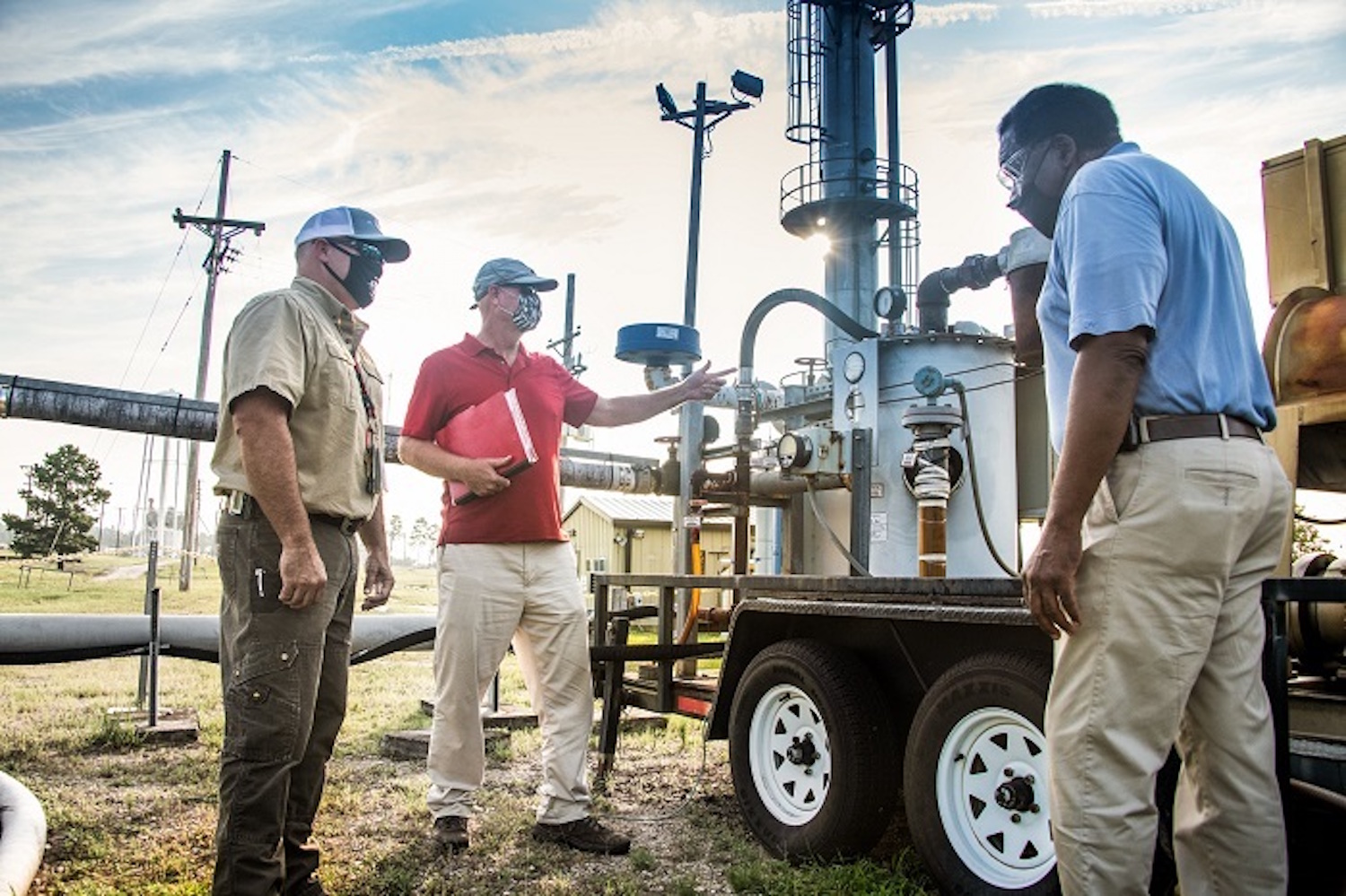
F Area operator Thomas Harman (left) and SRNS scientist Kevin Boerstler check the pumps, sensors, and piping that blend a base concentrate to inject into acidic groundwater at the Savannah River Site. (Photo: DOE)
The Savannah River Site is reducing the flow of hazardous and radioactive metal contaminants to South Carolina’s rivers and streams by injecting a mix of clean water and baking soda into the site’s groundwater. The base mix neutralizes groundwater that has become acidic as a result of SRS’s chemical separations work, helping restrict the flow of contaminants.
(Source: Screen shot from YouTube video)
While it has been known for decades that bacteria known as Geobacter could clean up uranium waste, researchers at Michigan State University recently uncovered the biological mechanism behind the bacteria’s ability to do it.
From left, SRNS mechanic Todd Cockrell, engineer John Bradley, and project manager Joao Cardoso-Neto plan the removal of a vapor extraction unit at the Savannah River Site. (Photo: DOE)
Department of Energy site contractors Savannah River Nuclear Solutions and Savannah River Remediation received high marks from a recent independent audit of their environmental management work at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina.
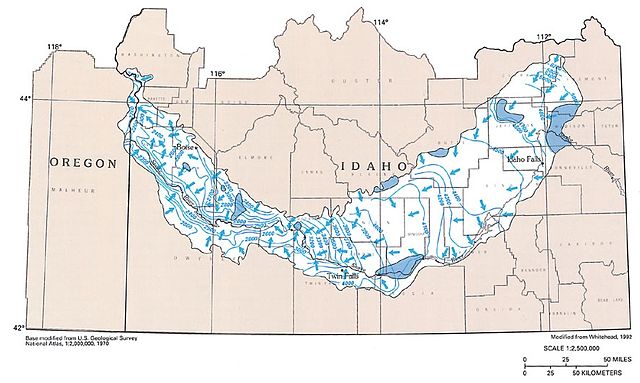
The Snake River Plain Aquifer
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management will award the Idaho Cleanup Project contract for the Idaho National Laboratory site to Idaho Environmental Coalition (IEC), of Tullahoma, Tenn. The contract has an estimated ceiling of approximately $6.4 billion over 10 years, with cost reimbursement and fixed-price task orders to define the contract performance.
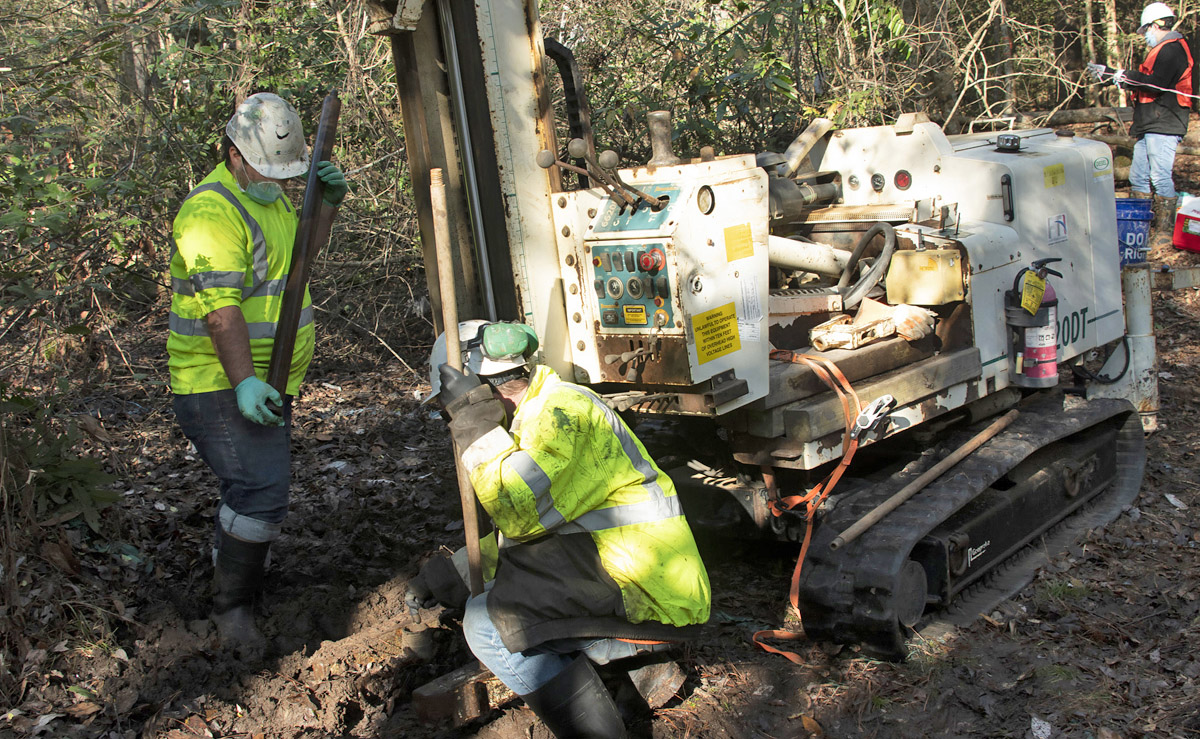
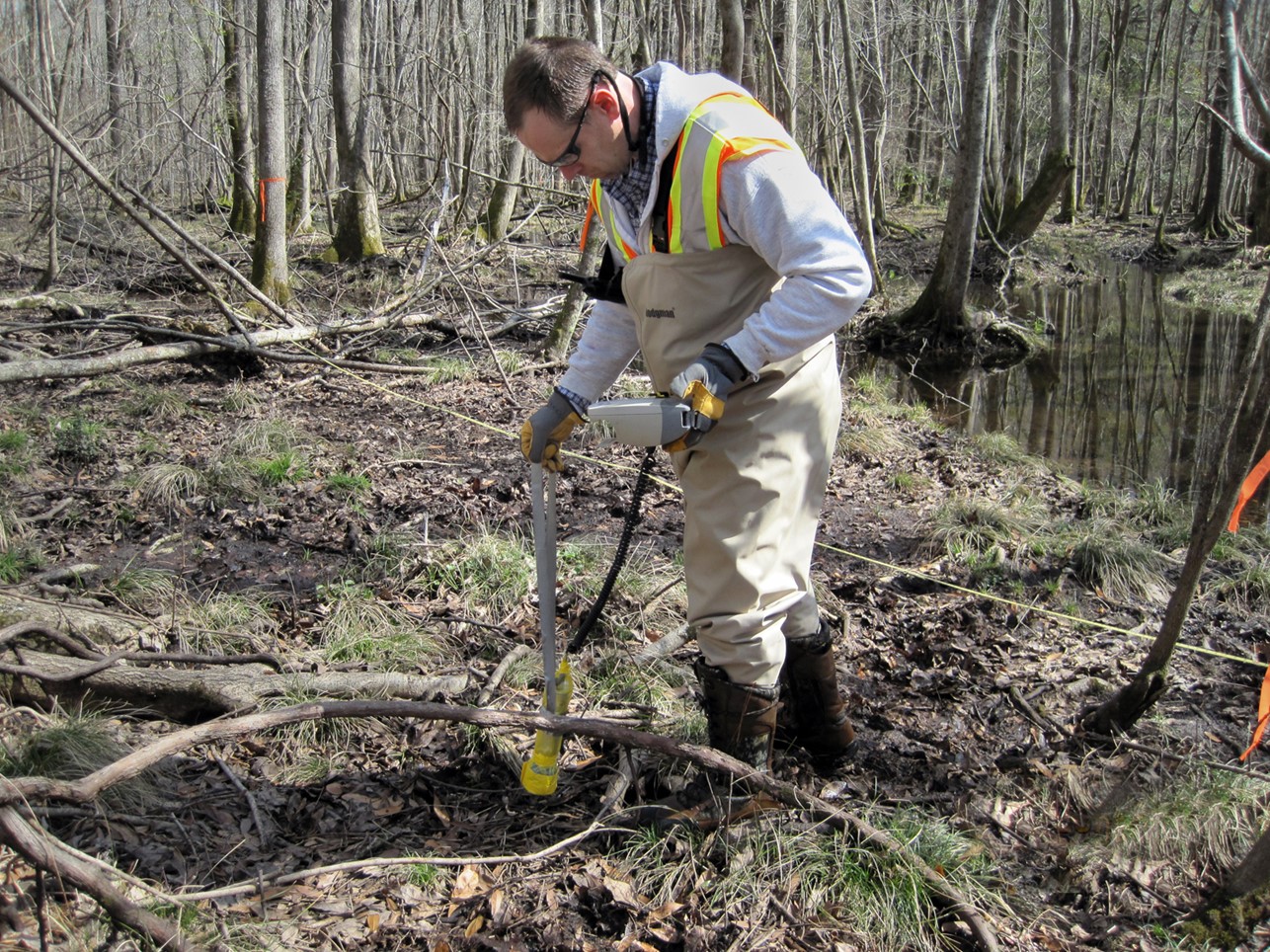
SRNS subcontractors Donald Miles and Richard Mooney drill for soil samples as part of a project to immobilize I-129 in the groundwater and soil at the Savannah River Site. Photo: DOE/SRNS
A silver chloride–based cleanup technology is expected to reduce radioactive iodine-129 contamination found in soil and groundwater near the center of the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina to levels well below regulatory limits. The I-129 was created during the production of plutonium and tritium at the site throughout the Cold War era.
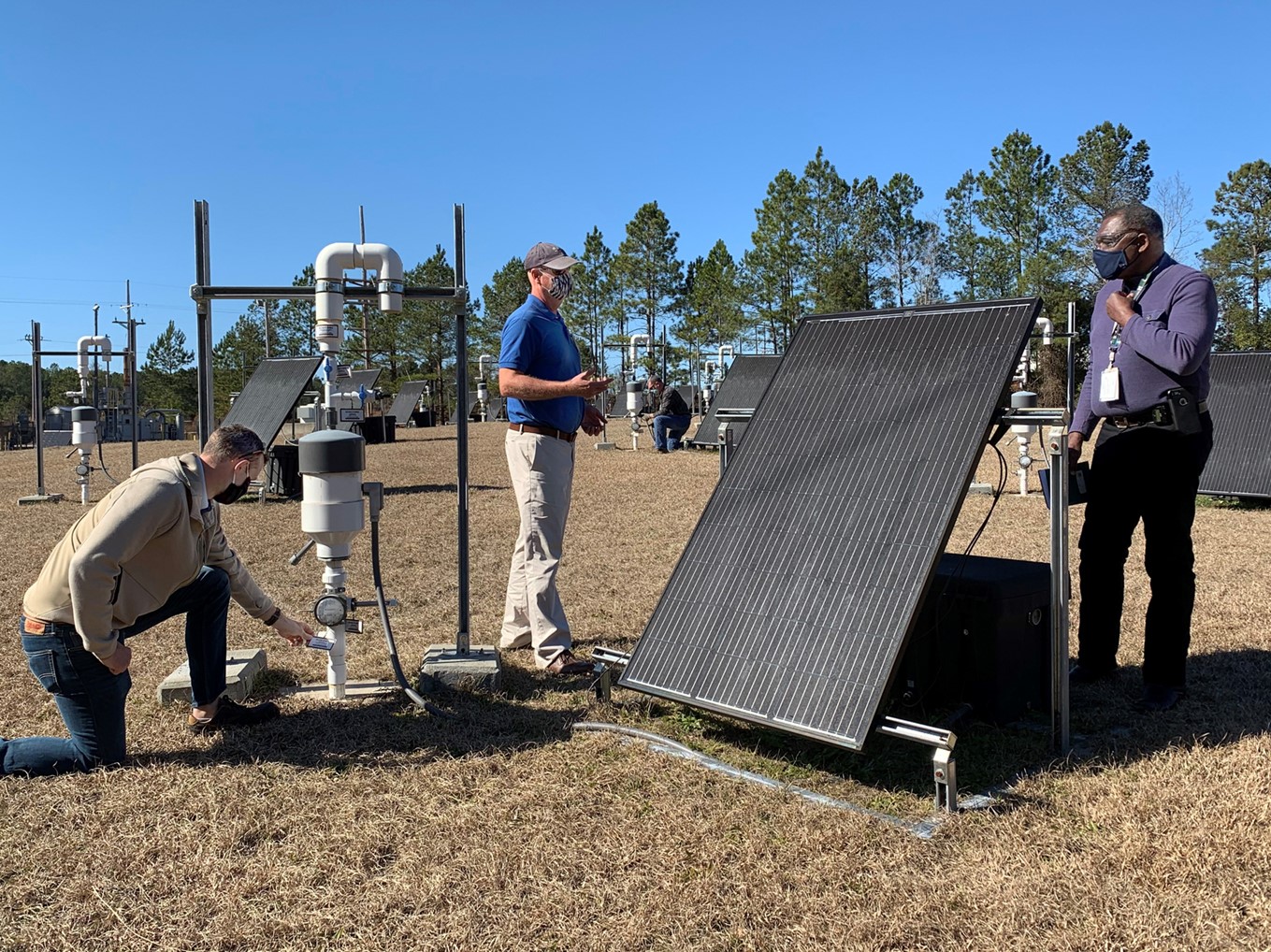
SRNS engineers (from left) Will Jolin, John Bradley, and Joao Cardoso-Neto discuss a plan to move and repurpose equipment used at 19 soil cleanup sites. Photo: DOE
A project to passively remove nonradioactive contaminants from the soil and groundwater at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina is coming to an end, as workers prepare to remove solar-power “plugs” from 19 soil remediation locations at the site.









 within the Hanford Site.png)

 and Andrew Thompson.jpg)